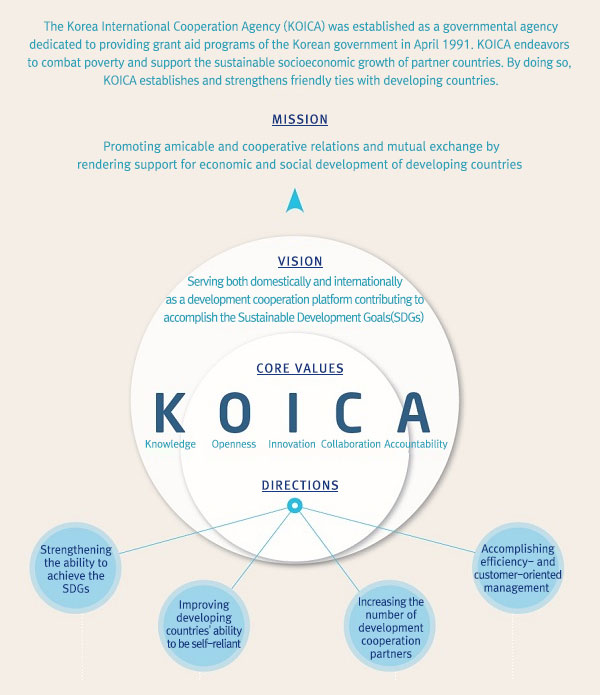
KOICA
Koica's ODA Framework
|
Korea’s ODA consists of three types of aid: 1) bilateral grants, 2) bilateral loans, and 3) multilateral assistance. Bilateral grant aid comprises of technical cooperation and various types of transfers (made in cash, goods, or services) with no obligation for repayment. Bilateral loans, on the other hand, are provided on concessional terms under the name of the Economic Development Cooperation Fund (EDCF). Lastly, multilateral assistance is delivered either as financial subscriptions or (grant) contributions to international organizations. In terms of ODA implementation, KOICA is responsible for Korea’s bilateral grant aid and technical cooperation programs while the Korea Export-Import Bank (Korea Eximbank) administers the EDCF loans. KOICA’s bilateral grant aid makes up around 74% of the total budget of Korea’s bilateral ODA. KOICA has 44 representative offices in 44 partner countries, and these overseas offices play a critical role in implementing KOICA’s aid programs at the field level. To maximize the effectiveness of our development cooperation, KOICA continuously collects and updates information on the needs and demands of partner countries through policy dialogues with various stakeholders and/or demand surveys conducted through Korean embassies and overseas offices. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs(MOFA) and the Ministry of Strategy and Finance (MOSF) are responsible for multilateral assistance. |
|
KOICA’s Legal Framework: Korea International Cooperation Agency Act The KOICA Act was enacted in 1991 to establish KOICA with the task of implementing Korea’s grant aid programs and promoting international cooperation. The Act provides a legal platform for KOICA’s grant aid programs, human resource management, and ODA policy implementation. According to the Act, KOICA’s grant aid programs include the following: (a) Project (b) Development consulting (c) Dispatch of human resources; (d) Education and training of human resources of countries for cooperation (e)Funding support for governments of countries for cooperation (f) Assistance in commodities and funds; (g)Public cooperation projects and public-private cooperation projects (h) Humanitarian assistance such as emergency relief, reconstruction and restoration, and prevention of disasters (i) Development cooperation with foreign institutions and international organizations (j) Research and development (k) Education, public relations, and human resources development. |
